A Guide to Increasing Problem-Solving Skills in Kids (with Examples)

In today’s fast-paced world, tackling challenges and finding innovative solutions is crucial for success. As parents and educators, it’s our responsibility to nurture this skill in children from an early age. By understanding the psychology behind problem-solving steps and implementing active strategies, we can help kids gain independence in solving problems effectively. Let’s explore practical ways to foster active problem-solving skills in young learners.
Importance of Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills are not just about finding the right answer; they involve critical thinking, creativity, and resilience. Children with strong problem-solving abilities are better equipped to handle academic tasks, navigate social situations, and excel in future careers. Moreover, problem-solving fosters a growth mindset, teaching children that setbacks are opportunities for learning and growth.
Understanding the Problem-Solving Process
Problem-solving is a dynamic cognitive process involving several interconnected steps, each crucial in reaching a satisfactory solution. Here’s a more detailed exploration of each step:
1. Identifying the Problem: The first step in problem-solving is accurately recognizing and defining the problem. Encourage children to articulate the problem in their own words, breaking it into manageable components. This step lays the foundation for the entire problem-solving process, as a clear understanding of the problem is essential for generating effective solutions.
2. Brainstorming Solutions: Children can brainstorm potential solutions once the problem is identified. Encourage creativity and open-mindedness during this phase, emphasizing that there are often multiple ways to approach a problem. Encourage children to think outside the box and consider unconventional solutions they may not have initially considered.
3. Evaluating Options: After generating a list of possible solutions, evaluating each option is important. Help children consider the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, weighing the potential risks and benefits. Encourage them to think about the feasibility of each option and how well it addresses the underlying problem.
4. Implementing a Plan: Once a suitable solution has been identified, it’s time to implement the plan. Guide children through the process of implementing their chosen solution, breaking down the steps into manageable tasks. Encourage them to stay organized and monitor their progress as they work towards solving the problem.
Doing tasks or chores and receiving star on a star chart for it would be great for learning to make plans.
5. Reflecting on the Outcome: After implementing the solution, reflecting on the outcome and evaluating its effectiveness is important. Did the solution achieve the desired result? What worked well, and what could be improved for future problem-solving endeavors? Encourage children to learn from their successes and failures, using each experience as an opportunity for growth and learning.
By teaching children these problem-solving steps, we provide them with a structured framework for approaching challenges with confidence and resilience. Through practice and experience, children can develop the skills and mindset necessary to tackle problems independently and effectively navigate the complexities of the world around them.
Promoting Active Problem-Solving
Encourage children to actively engage in problem-solving by involving them in real-life scenarios. Provide opportunities for hands-on exploration, encourage open-ended questions, and foster curiosity. When faced with a problem, resist the urge to provide immediate solutions; instead, guide children through the process of finding their own answers.
For more tips on helping your child resolve conflict situations, check out our article on conflict resolution for kids here.
Collaboration is an essential aspect of problem-solving. Encourage children to work together, share ideas, and consider different perspectives. Collaborative problem-solving enhances teamwork skills and exposes children to diverse strategies and approaches.
Problem-solving charts
Problem-solving charts can be invaluable tools for children to visually map out their thought processes and track their progress as they work through challenges. These charts provide a structured framework that breaks down the problem-solving process into manageable steps, making it easier for children to understand and follow. By using charts, children can organize their ideas, brainstorm solutions, and evaluate options systematically. A great example of these benefits is an “I Can” worksheet.
Additionally, problem-solving charts are a resource children can refer to when they encounter obstacles or feel stuck, helping them stay focused and motivated. Whether it’s a flowchart, a mind map, or a step-by-step guide, problem-solving charts provide a visual roadmap that empowers children to approach problems confidently and independently.
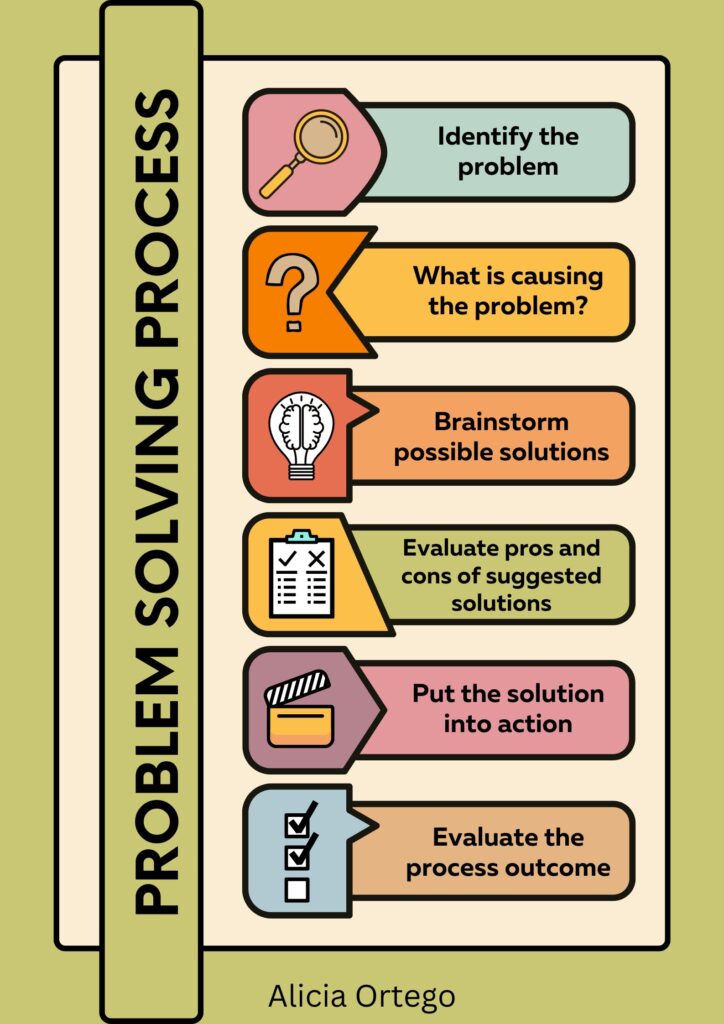
Here’s a ready made chart for you to use. Surely, there’s a Downloadable PDF
10 examples of problem-solving activities for kids
1. Building with Blocks: Provide children with a set of building blocks and challenge them to construct a specific structure or solve a design problem, such as building the tallest tower that can support a small weight.
2. Puzzle Solving: Offer a variety of puzzles, such as jigsaw puzzles, Sudoku, or logic puzzles, and encourage children to work through them independently or collaboratively to find solutions.
3. Science Experiments: Conduct simple science experiments that require problem-solving skills, such as creating a homemade volcano or designing a boat that can float and hold weight using only certain materials.
4. Escape Room Challenges: Set up an age-appropriate escape room scenario at home or in the classroom, where children must solve a series of puzzles and riddles to “escape” within a given time limit.
5. Creative Storytelling: Give children a prompt or a problem to solve through storytelling. Encourage them to use their imagination to create characters, settings, and plot twists that lead to a satisfying resolution.
6. Outdoor Treasure Hunt: Create a treasure map with clues leading children to different outdoor locations. They must use problem-solving skills to decipher the clues and find the hidden treasure.
7. Role-Playing Scenarios: Set up role-playing scenarios where children take on different roles and work together to solve a problem. For example, they could play doctors in a pretend hospital and diagnose and treat “patients” with various ailments.
8. Design Challenges: Provide children with materials such as cardboard, tape, and scissors, and challenge them to design and build a specific object, such as a bridge, a vehicle, or a robot, that meets certain criteria and functions correctly.
9. Math Games: Play math games that require problem-solving skills, such as “24 Game,” where players must use four numbers to make 24 using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
10. Community Service Projects: Engage children in community service projects that require problem-solving skills, such as organizing a food drive, planning a fundraising event, or designing a recycling program for their school.
These activities promote critical thinking and creativity and provide opportunities for children to develop resilience, teamwork, and perseverance as they work through challenges and find solutions.
Providing Support
While encouraging independent problem-solving skills is crucial, offering appropriate support and guidance to children as they navigate challenges is equally important. One way to provide support is by creating a supportive environment where children feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and ideas without fear of judgment. Encourage open communication and actively listen to children’s concerns, validating their feelings and offering reassurance when needed.
Additionally, offering encouragement and praise can boost children’s confidence and motivation to persist in problem-solving tasks. Acknowledge their efforts, no matter how small, and celebrate their achievements along the way. Recognizing and rewarding their perseverance and creative thinking can instill a sense of accomplishment and encourage them to continue tackling challenges with enthusiasm.
Moreover, being available to answer questions and offer suggestions is essential in helping children overcome obstacles they may encounter during the problem-solving process. Encourage children to seek help when needed and provide guidance without simply providing the answers. Instead, ask probing questions to prompt critical thinking and guide them toward finding solutions independently.
Furthermore, modeling problem-solving behaviors can be a powerful way to support children’s development of these skills. Share your problem-solving strategies and experiences, demonstrating perseverance, flexibility, and resilience in facing challenges. By serving as a positive role model, you can inspire children to approach problems with a growth mindset and the confidence to overcome obstacles.
In summary, providing support and guidance while promoting independent problem-solving skills is essential for children’s growth and development. By creating a nurturing environment, offering encouragement, being available to answer questions, and modeling problem-solving behaviors, we can empower children to become confident and capable problem solvers who are equipped to tackle challenges with resilience and creativity.
Conclusion
Empowering children to become confident problem solvers requires patience, creativity, and dedication. By understanding the psychology behind problem-solving steps and providing opportunities for active engagement, we can help kids develop essential skills for success. Let’s inspire the next generation of innovators, thinkers, and problem solvers.
More articles

Teaching Kids to Celebrate Differences Through Books
Why Books Matter in Teaching Kids About Differences Teaching kids to celebrate differences through books is one of the most effective and natural ways to build a more inclusive future. Stories have long served as windows into other lives, cultures, and perspectives. When children read books that highlight diversity, inclusion, and empathy, they begin to […]

How Technology Can Empower Your Kids to Learn, Grow, and Thrive
Technology often gets a bad rap when it comes to its effects on children, including issues related to screen time, cyberbullying, and online distractions. While these concerns are valid, these misconceptions should not overshadow its incredible potential to enhance education, creativity and well-being for your child when used responsibly and mindfully. When used appropriately, technology […]

Using Alicia Ortego’s Books in the Classroom: Tips and Examples
In today’s classrooms and after-school programs across America, teachers and educators are constantly looking for effective ways to support children’s social-emotional learning (SEL). Alicia Ortego’s My Superpower books have become a favorite tool for many educators to encourage kindness, mindfulness, confidence, and other important values in young learners. Here are some real-world-inspired ways teachers and […]



